
Default Stack Provisioning
✅ This template can be safely applied from any local work environment, even running outside an EWC tenancy's private network.
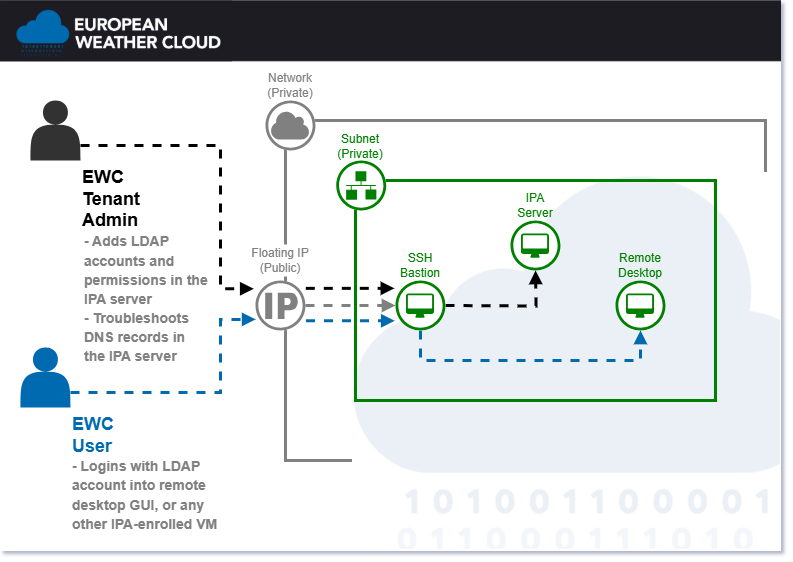
The default stack provides an integrated environment for secure access and centralized management in the European Weather Cloud (EWC). It orchestrates the deployment of an IPA server for LDAP and DNS functionality, an SSH bastion for access from the public internet, and a remote desktop for graphical interfacing, while ensuring both the bastion and desktop are enrolled as clients to the IPA server to centralize authentication, authorization, and resource discovery.
This configuration template (i.e., an Ansible Playbook) builds upon the individual templates for IPA server, SSH bastion, remote desktop, and IPA client to automate their deployment and integration.
Functionality
The template is designed to:
- Provision the IPA server instance via Terraform, including network validation and automatic subnet DNS updates to enable centralized user management and resource discovery across the environment.
- Provision the SSH bastion instance via Terraform, configured as a secure entrypoint with intrusion prevention.
- Enroll the newly provisioned SSH bastion as an IPA client, connecting it to the IPA server for centralized credentials and DNS resolution.
- Provision the remote desktop instance via Terraform, equipped for graphical access over varying bandwidths.
- Enroll the newly provisioned remote desktop as an IPA client, integrating it with the IPA server for unified access control.
After successful provisioning, you can leverage Terraform's functionality to modify or delete individual components safely. Each will have its own main.tf definition and terraform.tfstate state file under the corresponding user-defined local directories.
To learn the basics about managing infrastructure with Terraform, check out Terraform in 100 seconds on YouTube. You can also find a step-by-step example applied to the EWC on the official EWC documentation.
⚠️ Successful execution leads to changes of the DNS nameserver(s) in your OpenStack subnet (includes now only the IP address of the new IPA server). This can negatively affect existing VMs within your subnet. To prevent issues, programmatically update each VM via the IPA Client Enroll Flavour CommunityHub Item. Alternatively, you can manually add the new nameserver to their DNS configuration.
Prerequisites
- Install git (version 2.0 or higher )
- Install python (version 3.9 or higher)
- Install ansible (version 2.15 or higher)
- Install terraform (version 1.0 or higher)
- Get OpenStack API credentials (see How to request OpenStack Application Credentials section of the EWC documentation)
- Create an SSH keypair (see Creating Keys section of the EWC documentation)
- Import your public SSH key to OpenStack (see Import SSH Key section of the EWC documentation).
Usage
⚠️ Only RockyLinux versions 9 or 8 are supported due to constrains imposed by dependencies.
💡 VM plans with at least 4GB of RAM is recommended for successful setup and stable operation
⛔ Execution of this template can potentially affect DNS resolution on existing VMs within your subnet. To prevent issues, enroll them to the new IPA server via the IPA Client Enroll Flavour CommunityHub Item, OR manually edit nameservers in their DNS configuration.

1. Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/ewcloud/ewc-ansible-playbook-flavours-and-provisioning.git
1.1. Change to the specific Item's subdirectory
cd ewc-ansible-playbook-flavours-and-provisioning/playbooks/default-stack-provisioning
1.2. (Optional) Checkout an specific Item's version
⚠️ Make sure to replace
x.y.zin the command below, with your version of preference.
git checkout x.y.z
2. Download Ansible dependencies
💡 By default, Ansible Roles are installed under the
~/.ansible/rolesdirectory within your working environment.
Download the correct version of the Ansible dependencies, if you haven't done so already:
ansible-galaxy role install -r requirements.yml
3. Configure and apply the template
This template can be used interactively or non-interactively (i.e. with one single command to configure and also execute). Please beware that, regardless of your mode of choice, the complete execution may take several minutes, up to an hour.
3.1. Interactive Mode
By running the following command, you can trigger an interactive session that prompts you for the necessary user inputs, and then applies changes to your target EWC environment:
ansible-playbook default-stack-provisioning.yml
3.2. Non-Interactive Mode
💡 To learn more about defining variables at runtime, checkout the official Ansible documentation.
You can also run in non-interactive mode by passing the
--extra-vars or -e flag, followed by a map of key-value pairs; one for
each and every available input (see inputs section below). For example:
ansible-playbook \
-e '{
"ewc_provider":"eumetsat",
"public_keypair_name":"my-public-key-name",
"private_keypair_path":"~/.ssh/id_rsa",
"private_network_name":"private",
"security_group_name":"ipa",
"ipa_server_tf_project_path":"~/ewc/ipa-server-1",
"ipa_server_app_name":"ipa",
"ipa_server_instance_name":"server",
"ipa_server_instance_index": 1,
"ipa_server_hostname":"ipa-server-1",
"ipa_server_flavor_name":"eo1.large",
"ipa_server_image_name":"Rocky-8.10-20250604144456",
"ipa_domain":"eumetsat.sandbox.ewc",
"ipa_admin_username":"ipaadmin",
"ipa_admin_password":"my-secret-password",
"ipa_admin_givenname":"IPAADMIN",
"ipa_admin_surname":"EWC",
"ssh_bastion_tf_project_path":"~/ewc/ssh-bastion-1",
"ssh_bastion_app_name":"ssh",
"ssh_bastion_instance_name":"bastion",
"ssh_bastion_instance_index": 1,
"ssh_bastion_flavor_name":"eo1.large",
"ssh_bastion_image_name":"Rocky-9.5-20250604142417",
"remote_desktop_tf_project_path":"~/ewc/remote-desktop-1",
"remote_desktop_app_name":"remote",
"remote_desktop_instance_name":"desktop",
"remote_desktop_instance_index": 1,
"remote_desktop_flavor_name":"eo1.large",
"remote_desktop_image_name":"Rocky-9.5-20250604142417",
"remote_desktop_instance_has_fip":"yes",
"fail2ban_whitelisted_ip_ranges":""
}' \
default-stack-provisioning.yml
Inputs
| Name | Description | Type | Default | Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ewc_provider | your target EWC provider. Must match that the provider of your OpenStack application credentials. Valid input values are ecmwf or eumetsat. |
string |
eumetsat |
yes |
| public_keypair_name | name of public keypair (stored in OpenStack) to be copied into the instance for remote SSH access | string |
n/a | yes |
| private_keypair_path | path to the local private keypair to use for SSH access to the instance. | string |
~/.ssh/id_rsa |
yes |
| private_network_name | private network name to attach the instance | string |
private |
yes |
| security_group_name | security group name to apply to the instance | string |
ipa |
yes |
| ipa_server_tf_project_path | path to terraform working directory | string |
~/ewc/ipa-server-1 |
yes |
| ipa_server_app_name | application name, used as prefix in the full instance name | string |
ipa |
yes |
| ipa_server_instance_name | name of the instance, used in the full instance name | string |
server |
yes |
| ipa_server_instance_index | index or identifier for the instance, used as suffix in the full instance name | number |
1 |
yes |
| ipa_server_hostname | hostname of the IPA server. Should match the pattern "<ipa_server_app_name>-<ipa_server_instance_name>-<ipa_server_instance_index>". Required for input validation purpose | string |
ipa-server-1 |
yes |
| ipa_server_flavor_name | name the flavor to use for the instance. To learn about available options, checkout the official EWC VM plans documentation | string |
eo1.large |
yes |
| ipa_server_image_name | name of the image to use for the instance. For complete information on available options, see the official EWC Images documentation | string |
Rocky-8.10-20250604144456 |
yes |
| ipa_domain | domain name to be managed by the IPA server. Example: eumetsat.sandbox.ewc |
string |
n/a | yes |
| ipa_admin_username | username of administrator account to replace the default IPA admin | string |
ipaadmin |
yes |
| ipa_admin_password | password of administrator account to replace the default IPA admin | string |
n/a | yes |
| ipa_admin_givenname | given name of the administrator to replace the default IPA admin (needs not be a physical person) | string |
EWC |
yes |
| ipa_admin_surname | surname of the administrator to replace the default IPA admin (needs not to belong to a physical person) | string |
IPAADMIN |
yes |
| ssh_bastion_tf_project_path | path to terraform working directory | string |
~/ewc/ssh-bastion-1 |
yes |
| ssh_bastion_app_name | application name, used as prefix in the full instance name | string |
ssh |
yes |
| ssh_bastion_instance_name | name of the instance, used in the full instance name | string |
bastion |
yes |
| ssh_bastion_instance_index | index or identifier for the instance, used as suffix in the full instance name | number |
1 |
yes |
| ssh_bastion_flavor_name | name the flavor to use for the instance. To learn about available options, checkout the official EWC VM plans documentation | string |
eo1.large |
yes |
| ssh_bastion_image_name | name of the image to use for the instance. For complete information on available options, see the official EWC Images documentation | string |
Rocky-9.5-20250604142417 |
yes |
| remote_desktop_tf_project_path | path to terraform working directory | string |
~/ewc/remote-desktop-1 |
yes |
| remote_desktop_app_name | application name, used as prefix in the full instance name | string |
remote |
yes |
| remote_desktop_instance_name | name of the instance, used in the full instance name | string |
desktop |
yes |
| remote_desktop_instance_index | index or identifier for the instance, used as suffix in the full instance name | number |
1 |
yes |
| remote_desktop_flavor_name | name the flavor to use for the instance. To learn about available options, checkout the official EWC VM plans documentation | string |
eo1.large |
yes |
| remote_desktop_image_name | name of the image to use for the instance. For complete information on available options, see the official EWC Images documentation | string |
Rocky-9.5-20250604142417 |
yes |
| remote_desktop_instance_has_fip | technically required to temporarily assign a floating IP to the instance to securely connect from localhost during initial configuration. 💡 The template ensures to remove the floating IP during post-provisioning | string |
yes |
yes |
| fail2ban_whitelisted_ip_ranges | IPv4 ranges (in CIDR format) to be whitelisted in Fail2ban configuration. When in doubt, do not set. Example: ['10.0.0.0/24','192.168.1.0/24'] |
list(string) |
'' |
no |
